[Updated] MSRP Vs MAP: Strategies and Price Attributes in B2B eCommerce
Pricing is a hot topic among B2B companies and customers. Customers have expectations and profit margins that must be met. Channel conflict is also a concern. There are also many product configurations, value-added items, and promotions to keep track of.
Retailers can use the minimum advertised price (MAP) and manufacturer's suggested retail price (MSRP). This will allow them to control their pricing strategy and promote competition among selling partners.
This article will focus on the importance of MAP and MSRP pricing tools to B2B eCommerce distributors and manufacturers, and how online sellers can use them with OroCommerce.
The B2B Sellers Face a Challenge
Many brands struggle to keep a competitive pricing strategy in the face of online shoppers who demand more choice, lower prices and personalization.
Dealing with B2B customers is more difficult as they need to get a product of high quality that meets their requirements. In fact, according to an AMA study, getting a "fair price" was three times more important than getting the "lowest price" - and that is true for companies in parts distribution, raw materials, or engineering and construction.
B2C trends such as pricing preferences are rapidly gaining popularity, and they make their way into B2B. B2B customers demand personalized pricing, with the same discounts and promotions that they receive from B2C customers. However, when making B2B eCommerce application decisions, B2B sellers look past personalized promotions and look for the ability to personalize offers to customers based on the company, order volume, and past experiences.
Even before the pandemic, over B2B marketplace is giving rise to multi-vendor portals targeting whole ecosystems and industries. Amazon is still the preferred destination in many of these industries. It's harder to keep up with Amazon's heavy discounts for customers.
Manufacturers want to be able to compete with discounters like Amazon. Amazon allows retailers to offer lower margins in exchange for reaching a wider market. Manufacturers need to be consistent with pricing without negatively impacting their partner relationships or their margins. For these reasons, MSRP and MAP strategies are useful tools to help manufacturers maintain consistency, transparency, and level the playing for their retail partners.
Our products:
MSI multi-source-inventory-management-system
MSRP vs. MAP: Which Policy is Right for You?
Let's explore the differences between MSRP and MAP pricing and their relevance to B2B eCommerce. We'll also discuss how B2B manufacturers can make use of these pricing strategies to their advantage.
What is the MSRP?
The MSRP, or manufacturer's suggested retail pricing, is the best solution. Retailers are not permitted to force them to sell at fixed prices. It is the suggested retail price that you recommend to retailers and distributors for your products. MSRP allows you to control product pricing by setting a price standard, and pricing parity for all resale channels.
MSRP isn't set in stone, so retailers can sell products at the most profitable prices. Retailers will find it a great guideline since it includes all costs associated with selling the product. This includes manufacturing, distribution, and retailer markup.
Anyone who has ever bought a car knows that the MSRP is what dealers use to price their cars. The MSRP is crucial for car manufacturers. It's meant to provide transparent pricing, avoid price wars and maintain desired margins for dealers. This figure can't be fixed as it will depend on the invoice price, which is what the dealer initially pays to the manufacturer. It also depends on the availability and desirability of the car.
While the automotive industry is a complicated one, digital transformation is slowly making inroads here too, and pricing and financing transparency are becoming more important to buyers.
Retailers can and do charge less than the MSRP, just like car manufacturers. This is because the MSRP is often artificially inflated and retailers profit from that by advertising lower prices for their products to make consumers think they are getting a bargain.
Amazon allows sellers to set "list prices" and "your prices" to attract customers. The retailer will win regardless of whether the price is higher than the invoice or the wholesale cost.
However, there is one drawback. One retailer may aggressively discount a product to create a price war. This can devalue the product and cause a crisis for everyone. By setting MAP pricing, manufacturers can create a plan for prevention or mitigation.
What is MAP?
The minimum advertised price, or MAP, is the lowest price that resellers are allowed to advertise and publicly display their products. Resellers can still sell products at lower prices if they negotiate privately and adhere to the MAP. It places greater restrictions on sellers than MSRP. This allows manufacturers to preserve brand quality perception while keeping prices and profits in check.
As a way to manage relationships with resellers, manufacturers can use minimum advertised pricing. This allows them to specify the minimum requirements for their products. Manufacturers can use a MAP to route the proceeds of sales to themselves. This allows them transparency and control over value-added products.
It is easy to see why manufacturers follow a MAP policy. With eCommerce, retailers are able to undersell brick-and-mortar retailers. Resellers can be forced to discontinue carrying the product by consumers who are more likely to shop online for low prices. Retailers can make the brand less valuable by trying to get the lowest price.
An eCommerce seller cannot display a price below the minimum price agreed to in an agreement. To ensure compliance, manufacturers must invest in enforcement and monitoring. This can also include flexibility to accommodate all retailers and sellers.
If a product's price is higher than the MAP but coupons or promotions bring down the minimum amount, confusion can result. If you feel you are violating any of the terms of your agreement, you should consult your supplier and manufacturer.
So, as you see, the major difference between MAP and MSRP is how these strategies are applied. An MSRP strategy is best for products that are sold directly to end-users. It maintains the prices of your products, keeps potential or existing retailers happy, and preserves healthy margins. A MAP policy supports profitable resale channels by supporting them.
These policies should be included in the wholesaler and dealer agreements that both parties sign. Manufacturers should also dedicate resources to ensure that pricing policies are followed.
https://www.connectpos.com/top-free-bigcommerce-apps-for-online-stores/
https://www.connectpos.com/top-free-magento-extensions-for-users/
https://www.connectpos.com/best-retail-sales-tips/
OroCommerce and price attributes
OroCommerce's price parameters are custom parameters that allow you to specify price values per unit of quantity in different currencies. Examples of such attributes include MAP, MSRP and wholesale pricing.
What price attributes should be used? A product attribute is sufficient to be used for products that are sold in one unit or in one currency. If the product has multiple attributes (e.g., price per item, set or currency), price attributes can be helpful.
OroCommerce allows sellers to easily set up price attributes and store information. This could be the price of premium packaging, labor per pound, or raw material cost. These price attributes can then be used for calculating product prices. This is handy when calculating new price values using product assignment and price calculation rules.
Let's take a closer look at the creation and management of price attributes in OroCommerce.
OroCommerce Price Attributes
Imagine you want to keep track of the MSRP or MAP prices for all products. The system allows you to create price attributes and then import the price values across the entire product catalog.
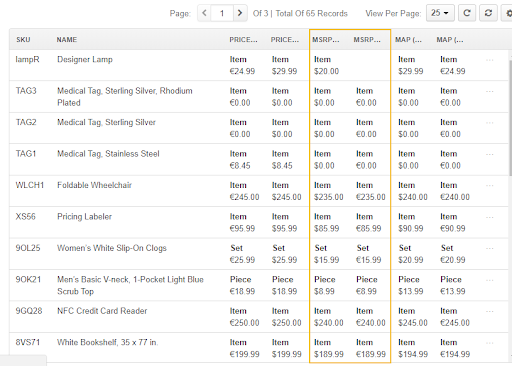
Go to Products, Price Attributes and click Create Price attribute.
Fill in the name of the attribute and the price attribute expression field. Select one or more Currencies and save the newly created Price Attribute.
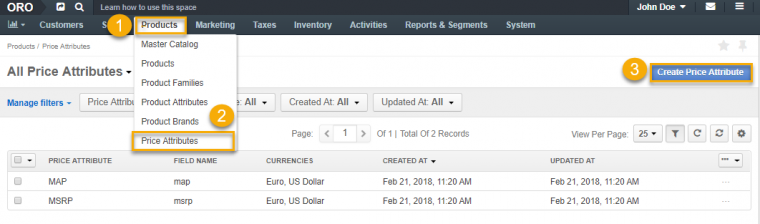
You can find more information about creating price attributes in our User Guide, Price Attributes.
After creating the price attribute, set the attributes values for each product. There are two methods to do this. You can first manually set product attributes by going to Products, Products and then hovering over More Actions until you click Edit.
Enter the currency value in the Product Pricing section on the product details page. Save your settings. Your price attribute can now be used in price list generation.
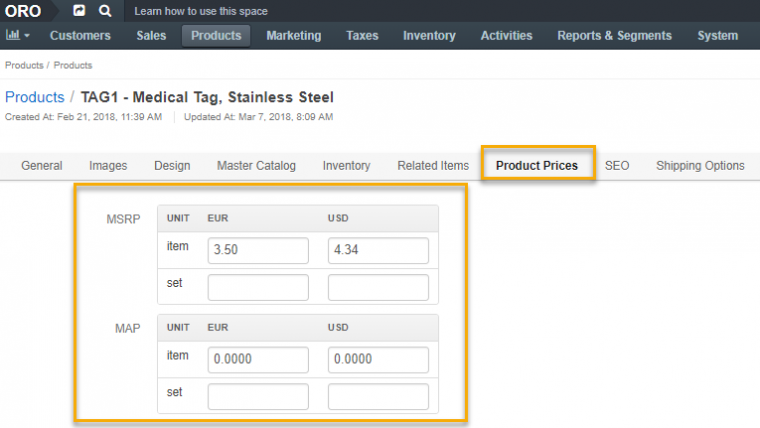
Read more about setting price attribute value in the User Guide.
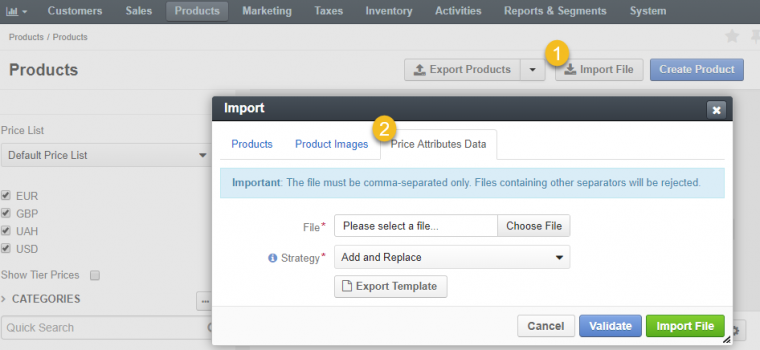
Bulk-importing products can be done by uploading a.csv file that has been prepared beforehand to add price attributes. This option is useful when you need to handle a lot of items at once. You have two options when importing the.csv file: either add or replace existing price attributes data, or delete all existing values and add new ones.
You can, for example, add the MSRP USD value previously missing to a product. Or you can replace it with the new one. Click Products, Products, Import file to import a bulk of product price attributes. Next, go to the Price Attributes data tab.
https://www.connectpos.com/low-cost-marketing-strategies-for-small-businesses/
https://www.connectpos.com/best-payment-methods-for-ecommerce-by-connectpos/
https://www.connectpos.com/top-4-social-media-for-selling-online/
You can see price attributes in action by watching the How to Set up Price Attributes video tutorial. This video tutorial will show you how to:
- Create a new MAP pricing attribute.
- You can manually set the MAP price attribute value of a product.
- To prepare your uploadable.csv file, use a template
- Validate the import results by importing a list price attribute values.
Also, make sure you watch this part of the Product Assignment and Price Calculation Rules video tutorial, as it shows how to calculate new price values specifically on the MSRP price.
MSRP and Map: Which Strategy Is Right for You?
Both a MSRP and MAP pricing strategy have their benefits, but there are also some disadvantages. For B2B companies that have prices that are sensitive to supply and demand cycles, or volatile raw material costs, MSRP may not be relevant in today's fast-paced market. Online sellers today need to be able to offer customized promotions, coupons, or discounts, while still adhering strictly with MAP pricing. Sellers must also enforce these policies or they risk damaging buyer confidence and brand value. In both cases, your pricing strategy requires a flexible B2B eCommerce platform so retailers can personalize across numerous channels.
It's possible to monitor reseller prices manually. However, OroCommerce, an eCommerce software that is customizable and B2B-specific, can help you and your resellers stick to your policies. You'll be able to adapt as your needs change, and you can keep your best relationships with trusted retailers.
Comments
Post a Comment